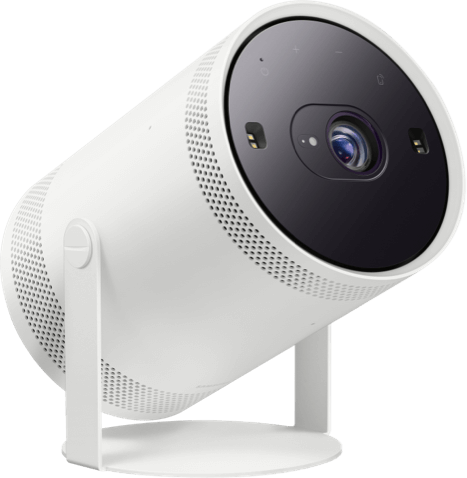
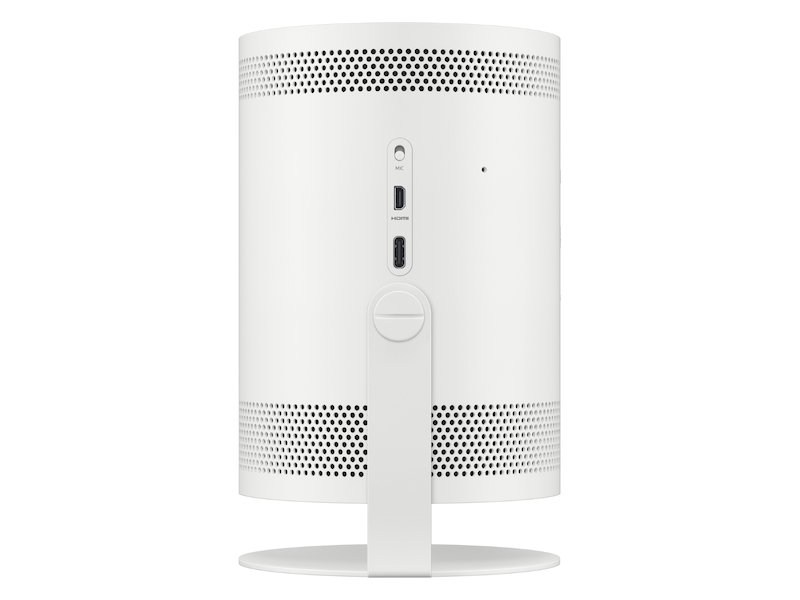
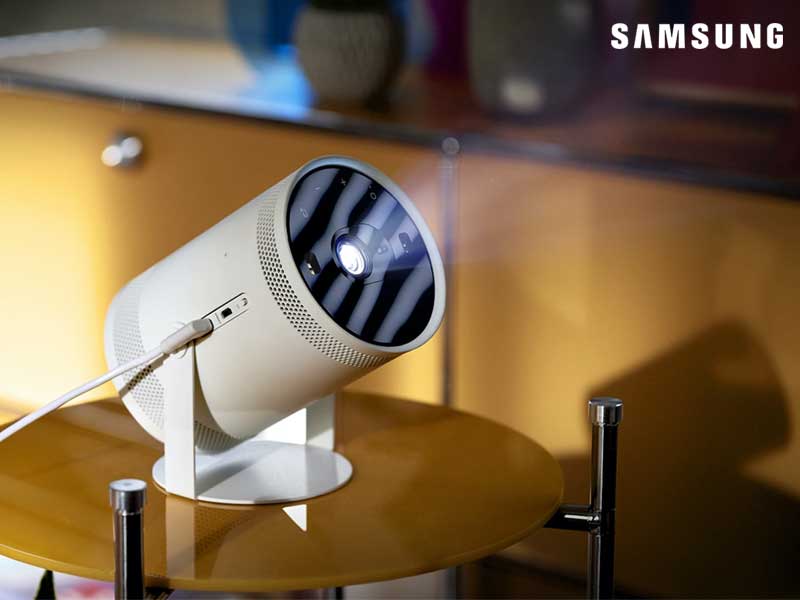
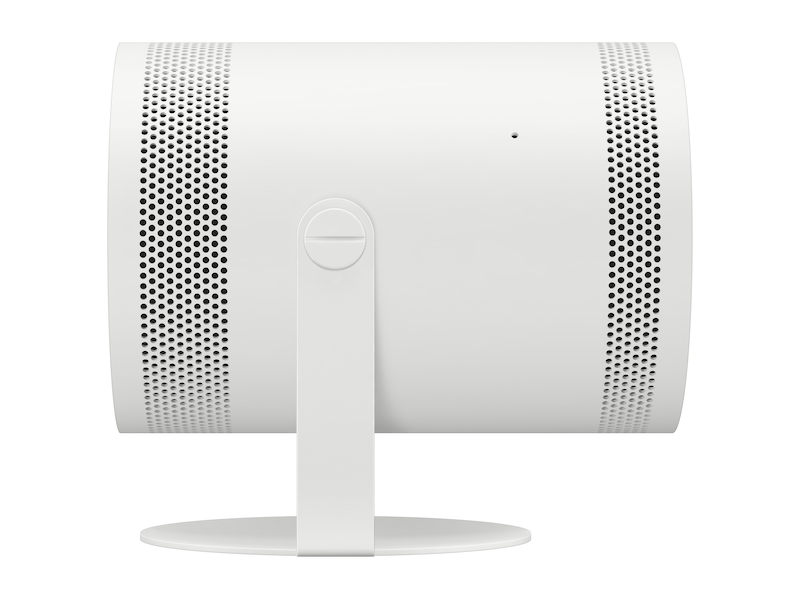
Amazon.com: SAMSUNG The Freestyle Skins for Smart Portable Projector, Device Cover Sleeve, 2022 Model, Coyote Beige : Electronics

Étui de Transport Rigide pour projecteur Samsung The Freestyle - Compatible avec Le projecteur Portable Samsung : Amazon.fr: High-Tech

Samsung Mobile Beam Projector EAD-R10 for Samsung Galaxy Devices – Specs, Availability | Projecteur telephone, Projecteur portable, Samsung
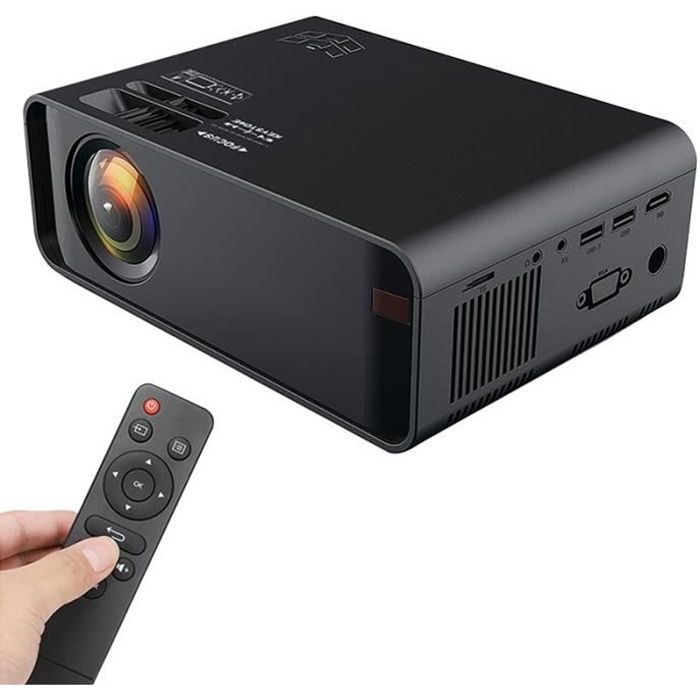

Mini projecteur 12000 Lumens TV Home Theatre 1080P Full HD - WiFi Vidéoprojecteur Portable pour iPhone Android Samsung USB VGA - Cdiscount TV Son Photo